PyVacy
PyVacy: Privacy Algorithms for PyTorch
Basically TensorFlow Privacy, but for PyTorch.
Example Usage
from pyvacy import optim, analysis, sampling
training_parameters = {
'N': len(train_dataset),
# An upper bound on the L2 norm of each gradient update.
# A good rule of thumb is to use the median of the L2 norms observed
# throughout a non-private training loop.
'l2_norm_clip': 1.0,
# A coefficient used to scale the standard deviation of the noise applied to gradients.
'noise_multiplier': 1.1,
# Each example is given probability of being selected with minibatch_size / N.
# Hence this value is only the expected size of each minibatch, not the actual.
'minibatch_size': 128,
# Each minibatch is partitioned into distinct groups of this size.
# The smaller this value, the less noise that needs to be applied to achieve
# the same privacy, and likely faster convergence. Although this will increase the runtime.
'microbatch_size': 1,
# The usual privacy parameter for (ε,δ)-Differential Privacy.
# A generic selection for this value is 1/(N^1.1), but it's very application dependent.
'delta': 1e-5,
# The number of minibatches to process in the training loop.
'iterations': 15000,
}
model = nn.Sequential(...)
optimizer = optim.DPSGD(params=model.parameters(), **training_parameters)
epsilon = analysis.epsilon(**training_parameters)
loss_function = ...
minibatch_loader, microbatch_loader = sampling.get_data_loaders(**training_parameters)
for X_minibatch, y_minibatch in minibatch_loader(train_dataset):
optimizer.zero_grad()
for X_microbatch, y_microbatch in microbatch_loader(TensorDataset(X_minibatch, y_minibatch)):
optimizer.zero_microbatch_grad()
loss = loss_function(model(X_microbatch), y_microbatch)
loss.backward()
optimizer.microbatch_step()
optimizer.step()
Tutorials
mnist.py
Implements a basic classifier for identifying which digit a given MNIST image corresponds to. The model achieves a test set classification accuracy of 96.7%. The model architecture and results achieved are inspired by the corresponding tutorial within TensorFlow privacy.
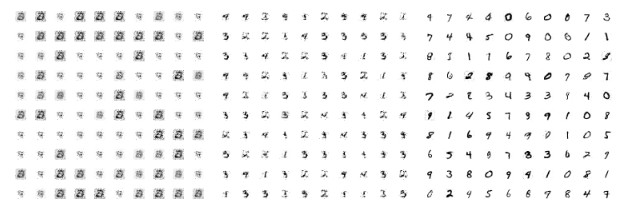
gan.py
Implements a Wasserstein GAN, in which the discriminator is trained via differentially private stochastic gradient descent. Generated images are plotted as a function of increasing epsilon (ɛ = 0.8, 3.0, 8.0).
Disclaimer
Do NOT use the contents of this repository in applications which handle sensitive data. The author accepts no liability for privacy infringements - use the contents of this repository solely at your own discretion.


