Visual Automata
Visual Automata is a Python 3 library built as a wrapper for the Automata library to add more visualization features.
Prerequisites
pip install automata-lib
pip install pandas
pip install graphviz
pip install colormath
pip install jupyterlab
Installing
Finite Automaton (FA)
VisualDFA
Importing
Import needed classes.
from automata.fa.dfa import DFA
from visual_automata.fa.dfa import VisualDFA
Instantiating DFAs
Define an visual_automata DFA that can accept any string ending with 00 or 11.
dfa = VisualDFA(
states={"q0", "q1", "q2", "q3", "q4"},
input_symbols={"0", "1"},
transitions={
"q0": {"0": "q3", "1": "q1"},
"q1": {"0": "q3", "1": "q2"},
"q2": {"0": "q3", "1": "q2"},
"q3": {"0": "q4", "1": "q1"},
"q4": {"0": "q4", "1": "q1"},
},
initial_state="q0",
final_states={"q2", "q4"},
)
Converting
An automata-lib DFA can be converted to a VisualDFA.
Define an automata-lib DFA that can accept any string ending with 00 or 11.
dfa = DFA(
states={"q0", "q1", "q2", "q3", "q4"},
input_symbols={"0", "1"},
transitions={
"q0": {"0": "q3", "1": "q1"},
"q1": {"0": "q3", "1": "q2"},
"q2": {"0": "q3", "1": "q2"},
"q3": {"0": "q4", "1": "q1"},
"q4": {"0": "q4", "1": "q1"},
},
initial_state="q0",
final_states={"q2", "q4"},
)
Convert automata-lib DFA to VisualDFA.
dfa = VisualDFA(dfa)
Transition Table
Outputs the transition table for the given DFA.
dfa.table
0 1
→q0 q3 q1
q1 q3 *q2
*q2 q3 *q2
q3 *q4 q1
*q4 *q4 q1
Minimal-DFA
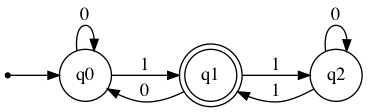
Creates a minimal DFA which accepts the same inputs as the old one. Unreachable states are removed and equivalent states are merged. States are renamed by default.
new_dfa = VisualDFA(
states={'q0', 'q1', 'q2'},
input_symbols={'0', '1'},
transitions={
'q0': {'0': 'q0', '1': 'q1'},
'q1': {'0': 'q0', '1': 'q2'},
'q2': {'0': 'q2', '1': 'q1'}
},
initial_state='q0',
final_states={'q1'}
)
new_dfa.table
0 1
→q0 q0 *q1
*q1 q0 q2
q2 q2 *q1
new_dfa.show_diagram()
minimal_dfa = VisualDFA.minify(new_dfa)
minimal_dfa.show_diagram()
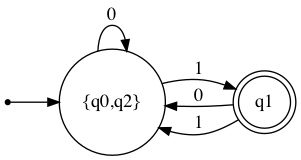
minimal_dfa.table
0 1
→{q0,q2} {q0,q2} *q1
*q1 {q0,q2} {q0,q2}
Check input strings
1001 does not end with 00 or 11, and is therefore Rejected
dfa.input_check("1001")
[Rejected]
Step: Current state: Input symbol: New state:
1 →q0 1 q1
2 q1 0 q3
3 q3 0 *q4
4 *q4 1 q1
10011 does end with 11, and is therefore Accepted
dfa.input_check("10011")
[Accepted]
Step: Current state: Input symbol: New state:
1 →q0 1 q1
2 q1 0 q3
3 q3 0 *q4
4 *q4 1 q1
5 q1 1 *q2
Show Diagram
For IPython dfa.show_diagram() may be used.
For a python script dfa.show_diagram(view=True) may be used to automatically view the graph as a PDF file.
dfa.show_diagram()
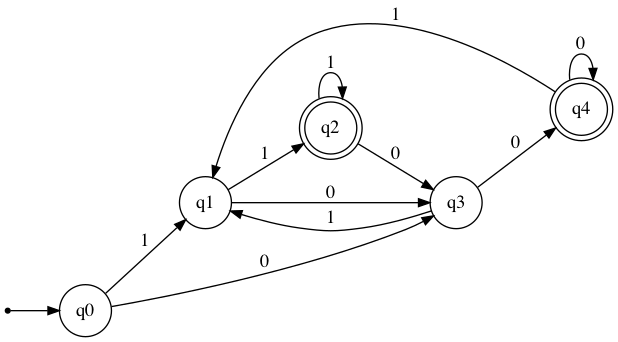
The show_diagram method also accepts input strings, and will return a graph with gradient red arrows for Rejected results, and gradient green arrows for Accepted results. It will also display a table with transitions states stepwise. The steps in this table will correspond with the [number] over each traversed arrow.
Please note that for visual purposes additional arrows are added if a transition is traversed more than once.
dfa.show_diagram("1001")
[Rejected]
Step: Current state: Input symbol: New state:
1 →q0 1 q1
2 q1 0 q3
3 q3 0 *q4
4 *q4 1 q1
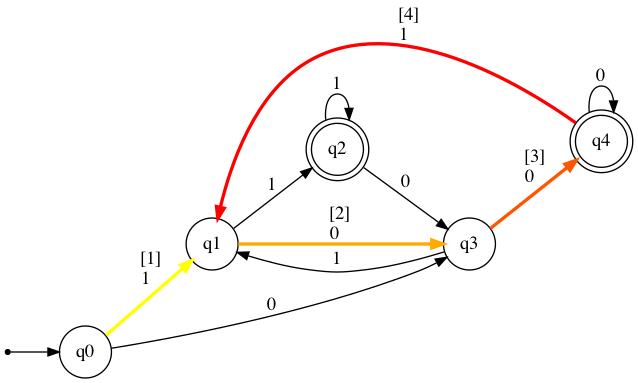
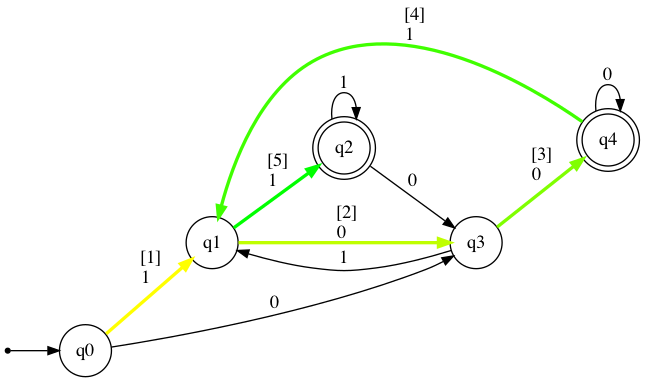
dfa.show_diagram("10011")
[Accepted]
Step: Current state: Input symbol: New state:
1 →q0 1 q1
2 q1 0 q3
3 q3 0 *q4
4 *q4 1 q1
5 q1 1 *q2
VisualNFA
Importing
Import needed classes.
from automata.fa.nfa import NFA
from visual_automata.fa.nfa import VisualNFA
Instantiating NFAs
Define an visual_automata NFA that can accept any string with the pattern 10, 1010, 101010.
nfa = VisualNFA(
states={"q0", "q1", "q2"},
input_symbols={"0", "1"},
transitions={
"q0": {"": {"q2"}, "1": {"q1"}},
"q1": {"1": {"q2"}, "0": {"q0", "q2"}},
"q2": {},
},
initial_state="q0",
final_states={"q0"},
)
Converting
An automata-lib NFA can be converted to a VisualNFA.
Define an automata-lib NFA that can accept any string with the pattern 10, 1010, 101010.
nfa = NFA(
states={"q0", "q1", "q2"},
input_symbols={"0", "1"},
transitions={
"q0": {"": {"q2"}, "1": {"q1"}},
"q1": {"1": {"q2"}, "0": {"q0", "q2"}},
"q2": {},
},
initial_state="q0",
final_states={"q0"},
)
Convert automata-lib NFA to VisualNFA.
nfa = VisualNFA(nfa)
Transition Table
Outputs the transition table for the given DFA.
nfa.table
0 1 λ
→*q0 ∅ q1 q2
q1 {*q0,q2} q2 ∅
q2 ∅ ∅ ∅
Eliminate lambda/epsilon
Creates a NFA with lambda transitions removed.
nfa_eliminated = VisualNFA.eliminate_lambda(nfa)
nfa_eliminated.table
0 1
→*q0 ∅ q1
q1 {*q0,q2} q2
q2 ∅ ∅
nfa_eliminated.show_diagram()
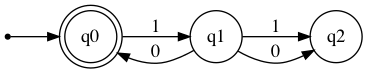
Check input strings
101 does not correspond with the pattern 10, 1010, 101010, and is therefore Rejected
nfa.input_check("101")
[Rejected]
Step: Current state: Input symbol: New state:
1 →*q0 1 q1
2 q1 0 q2
3 q2 1 ∅
1010 does correspond with the pattern 10, 1010, 101010, and is therefore Accepted
nfa.input_check("1010")
[Accepted]
Step: Current state: Input symbol: New state:
1 →*q0 1 q1
2 q1 0 →*q0
3 →*q0 1 q1
4 q1 0 →*q0
Show Diagram
For IPython nfa.show_diagram() may be used.
For a python script nfa.show_diagram(view=True) may be used to automatically view the graph as a PDF file.
nfa.show_diagram()
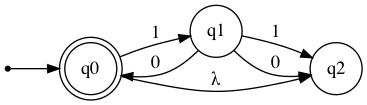
The show_diagram method also accepts input strings, and will return a graph with gradient red arrows for Rejected results, and gradient green arrows for Accepted results. It will also display a table with transitions states stepwise. The steps in this table will correspond with the [number] over each traversed arrow.
Please note that for visual purposes additional arrows are added if a transition is traversed more than once.
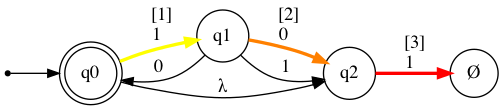
nfa.show_diagram("101")
[Rejected]
Step: Current state: Input symbol: New state:
1 →*q0 1 q1
2 q1 0 q2
3 q2 1 ∅
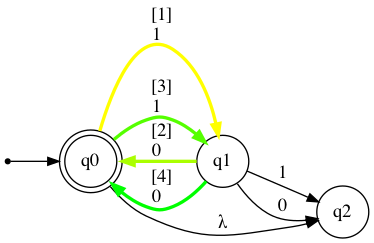
nfa.show_diagram("1010")
[Accepted]
Step: Current state: Input symbol: New state:
1 →*q0 1 q1
2 q1 0 →*q0
3 →*q0 1 q1
4 q1 0 →*q0
Please note that for long input strings, the path calculations may take some time.
big_nfa = VisualNFA(
states={"q1", "q2", "q3", "q4", "q5", "q6", "q7", "q8"},
input_symbols={"A", "C", "G", "T"},
transitions={
"q1": {"A": {"q7"}, "C": {"q4"}, "G": {"q4", "q2"}, "T": {"q4"}},
"q2": {"A": {"q3", "q6"}, "C": {"q2", "q4"}, "G": {"q3", "q6"}, "T": {"q6"}},
"q3": {"A": {"q8"}, "C": {"q8"}, "T": {"q8"}},
"q4": {"A": {"q5"}, "C": {"q4"}, "G": {"q5"}, "T": {"q2", "q4", "q5"}},
"q5": {"A": {"q3", "q8"}, "C": {"q3", "q8"}, "G": {"q8"}, "T": {"q3", "q8"}},
"q6": {"A": {"q8"}, "C": {"q8"}, "G": {"q8"}, "T": {"q8"}},
"q7": {"A": {"q7", "q8"}, "C": {"q7", "q8"}, "G": {"q8"}, "T": {"q3", "q8"}},
"q8": {},
},
initial_state="q1",
final_states={"q8"},
)
big_nfa.table
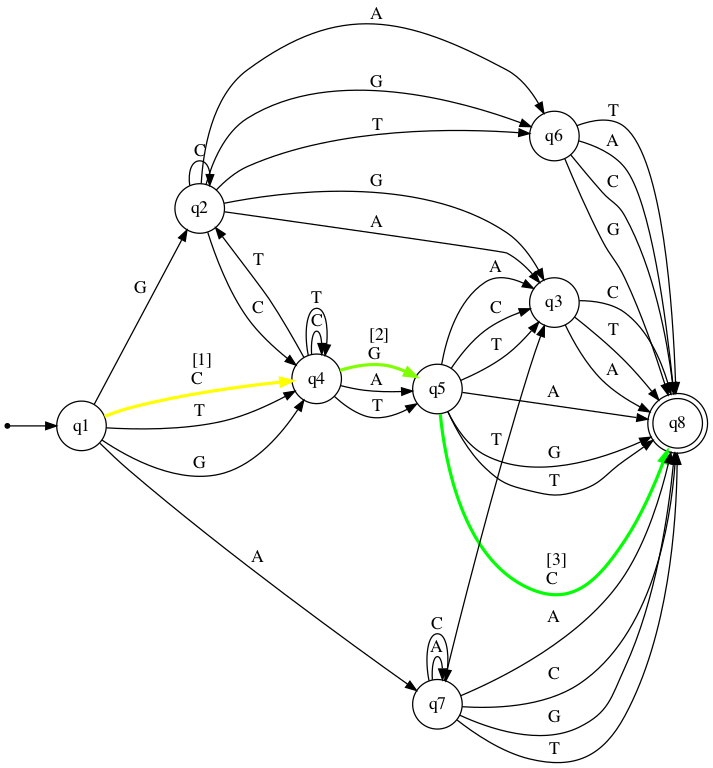
big_nfa.show_diagram("CGC")
[Accepted]
Step: Current state: Input symbol: New state:
1 →q1 C q4
2 q4 G q5
3 q5 C *q8
Authors
Lewi Lie Uberg - uberg.me