Project Lightspeed
A self contained OBS -> FTL -> WebRTC live streaming server. Comprised of 3 parts once configured anyone can achieve sub-second OBS to the browser livestreaming
Project Lightspeed is a fully self contained live streaming server. With Lightspeed you will be able to deploy your own sub-second latency live streaming platform. The Lightspeed repository contains the instructions for installing and deploying the entire application. So far, Lightspeed includes an ingest service, broadcast service via webRTC and a web application for viewing. Lightspeed is however completely modular. What this means is that you can write your own web app, ingest server or broadcast server. As of right now it is not as modular as it could be and I will be working on improving that in the future.
How It Works
Lightspeed Ingest listens on port 8084 which is the port used by the FTL protocol. Upon receiving a connection it completes the FTL handshake and negotiates a port (this is currently bugged however and defaults to 65535). Once the negotiation is done Lightspeed WebRTC listens on the negotiated port (in the future Lightspeed WebRTC will listen on the loopback interface so the ingest has more control on what packets we accept) and relays the incoming RTP packets over WebRTC. Lightspeed React communicates via websocket with Lightspeed WebRTC to exchange ICE Candidates and once a connection is established the video can be viewed.
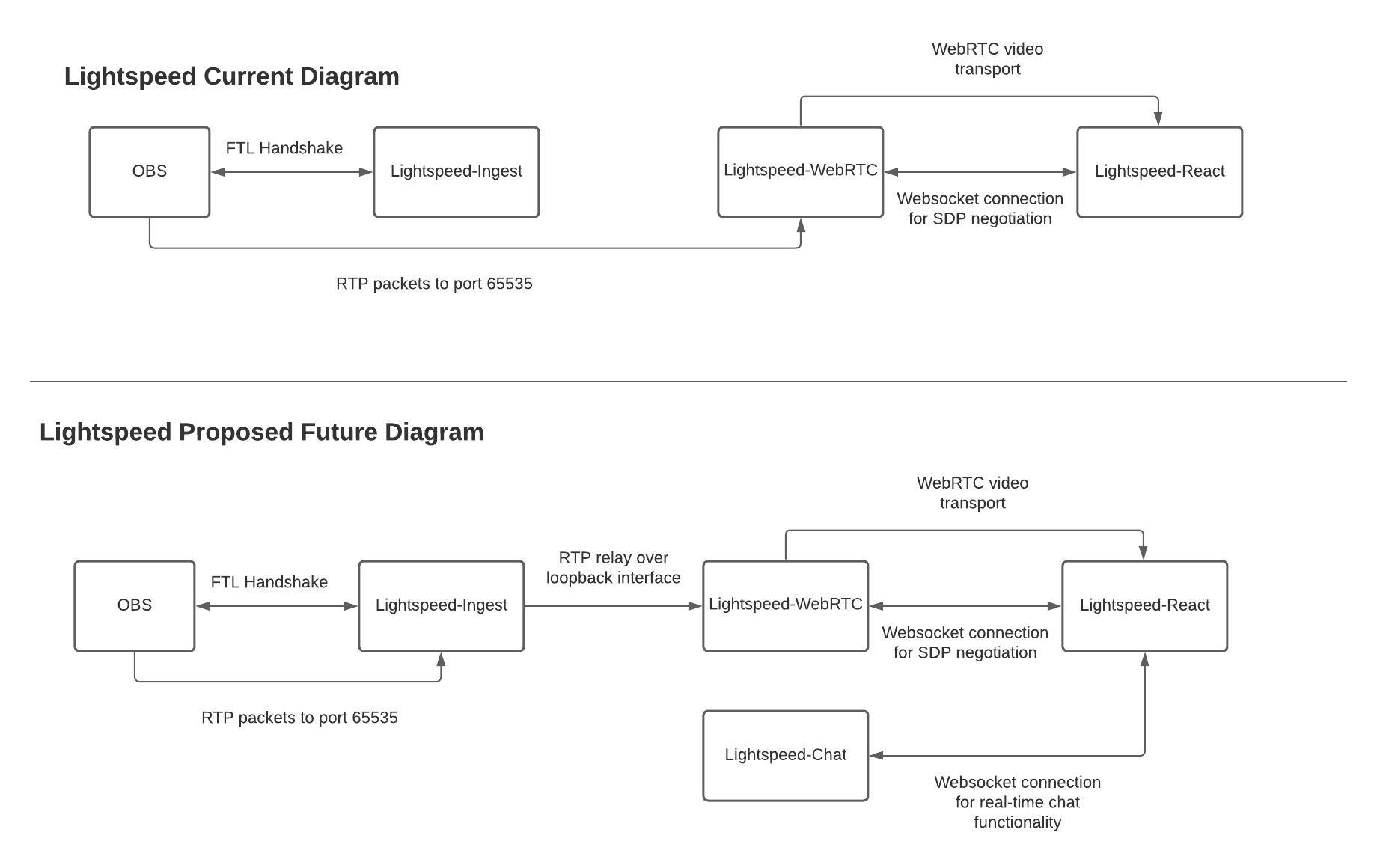
Diagram
Here is a diagram that outlines the current implementation and the future implementation that I would like to achieve. The reason I want the packets relayed from Ingest to WebRTC on the loopback interface is so that we have more control over who can send packets. Meaning that when a DISCONNECT command is recieved we can terminate the UDP listener so that someone could not start sending packets that we do not want
Built With
- Rust
- Golang
- React
Components
Discord
We now have a Discord server! This is a great way to stay up to date with the project and join in on the conversation! Come stop by!
Getting Started
In order to get Lightspeed running you will need to install all 3 repositories. There are installation instructions in each repository however I will include them here for the sake of simplicity.
Prerequisites
In order to run Lightspeed, Golang, Rust, and npm are required. Additionally the Rust repo requires a C compiler. If you get a linker cc not found error then you need to install a C compiler.
Installation
Lightspeed Ingest
git clone https://github.com/GRVYDEV/Lightspeed-ingest.git
cd Lightspeed-ingest
cargo build
Lightspeed WebRTC
Using go get
export GO111MODULE=on
go get github.com/GRVYDEV/lightspeed-webrtc
Using git
git clone https://github.com/GRVYDEV/Lightspeed-webrtc.git
cd Lightspeed-webrtc
export GO111MODULE=on
go build
Lightspeed React
git clone https://github.com/GRVYDEV/Lightspeed-react.git
cd Lightspeed-react
npm install
Usage
Lightspeed Ingest
cd Lightspeed-ingest
cargo run --release
Lightspeed WebRTC
Using go get
lightspeed-webrtc --addr=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
Using git
cd Lightspeed-webrtc
go build
./lightspeed-webrtc --addr=XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
Arguments
| Argument | Supported Values | Notes |
|---|---|---|
--addr |
A valid IP address | This is the local Ip address of your machine. It defaults to localhost but should be set to your local IP. For example 10.17.0.5 This is where the server will listen for UDP packets and where it will host the websocket endpoint for SDP negotiation |
Lightspeed React
You should then configure the websocket URL in config.json in the build directory. If you are using an IP then it will be the public IP of your machine if you have DNS then it will be your hostname.
Note: The websocket port is hardcoded meaning that Lightspeed-webrtc will always serve it on port 8080 (this may change in the future) so for the websocket config it needs to be `ws://IP_or_Hostname:8080/websocket
You can host the static site locally using serve which can be found here
Note: your version of serve may require the -p flag instead of -l for the port
cd Lightspeed-react
npm run build
serve -s build -l 80
The above will serve the build folder on port 80.
View Lightspeed in your web browser by visiting http://hostname or http://your.ip.address.here
Streaming From OBS
By default since we are using the FTL protocol you cannot just use a custom server. You will need to edit your services.json file. It can be found at:
Note: Not all versions of Linux have access to OBS with the FTL SDK built in. If you are on Linux and you cannot stream to Lightspeed this may be the issue.
Linux: ~/.config/obs-studio/plugin_config/rtmp-services/services.json
Windows: %AppData%\obs-studio\plugin_config\rtmp-services\services.json
Mac: /Users/YOURUSERNAME/Library/Application\ Support/obs-studio/plugin_config/rtmp-services/services.json
Paste the below into the services array and change the url to either the IP or the hostname of your Project Lightspeed server
Note: for the url it is not prefaced by anything. For example, given an IP of 10.0.0.2 you would put "url": "10.0.0.2" You do not need to indicate a port since the FTL protocol always uses 8084
{
"name": "Project Lightspeed",
"common": false,
"servers": [
{
"name": "SERVER NAME HERE",
"url": "your.lightspeed.hostname"
}
],
"recommended": {
"keyint": 2,
"output": "ftl_output",
"max audio bitrate": 160,
"max video bitrate": 8000,
"profile": "main",
"bframes": 0
}
},
After restarting OBS you should be able to see your service in the OBS settings pane
(Special Thanks to Glimesh for these instructions)
Stream Key
We are no longer using a default streamkey! If you are still using one please pull from master on the Lightspeed-ingest repository. Now, by default on first time startup a new streamkey will be generated and output to the terminal for you. In order to regenerate this key simply delete the file it generates called hash. In a Docker context we will work to make the key reset process as easy as possible. Simply copy the key output in the terminal to OBS and you are all set! This key WILL NOT change unless the hash file is deleted.

Help
This project is still very much a work in progress and a lot of improvements will be made to the deployment process. If something is unclear or you are stuck there are two main ways you can get help.
- Discord - this is the quickest and easiest way I will be able to help you through some deployment issues.
- Create an Issue - this is another way you can bring attention to something that you want fixed.
Roadmap
I will be fleshing out the roadmap in the coming days. As of right now I want to get Lightspeed to a point where it is as close to other live streaming services as possible. If there are any features that you want to see then feel free to suggest them!
See the open issues for a list of proposed features (and known issues).
Bugs
I am very far from perfect and there are bound to be bugs and things I've overlooked in the installation process. Please add issues and feel free to reach out if anything is unclear. If Lightspeed gets enough attention I can make a Discord server where I can more easily interact with people.



