DiffSinger - PyTorch Implementation
PyTorch implementation of DiffSinger: Diffusion Acoustic Model for Singing Voice Synthesis (TTS Extension).
Status (2021.06.03)
- [x] Naive Version of DiffSinger
- [ ] Shallow Diffusion Mechanism: Training boundary predictor by leveraging pre-trained auxiliary decoder + Training denoiser using
kas a maximum time step
Quickstart
Dependencies
You can install the Python dependencies with
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Inference
You have to download the pretrained models and put them in output/ckpt/LJSpeech/.
For English single-speaker TTS, run
python3 synthesize.py --text "YOUR_DESIRED_TEXT" --restore_step 160000 --mode single -p config/LJSpeech/preprocess.yaml -m config/LJSpeech/model.yaml -t config/LJSpeech/train.yaml
The generated utterances will be put in output/result/.
Batch Inference
Batch inference is also supported, try
python3 synthesize.py --source preprocessed_data/LJSpeech/val.txt --restore_step 160000 --mode batch -p config/LJSpeech/preprocess.yaml -m config/LJSpeech/model.yaml -t config/LJSpeech/train.yaml
to synthesize all utterances in preprocessed_data/LJSpeech/val.txt
Controllability
The pitch/volume/speaking rate of the synthesized utterances can be controlled by specifying the desired pitch/energy/duration ratios.
For example, one can increase the speaking rate by 20 % and decrease the volume by 20 % by
python3 synthesize.py --text "YOUR_DESIRED_TEXT" --restore_step 160000 --mode single -p config/LJSpeech/preprocess.yaml -m config/LJSpeech/model.yaml -t config/LJSpeech/train.yaml --duration_control 0.8 --energy_control 0.8
Training
Datasets
The supported datasets are
- LJSpeech: a single-speaker English dataset consists of 13100 short audio clips of a female speaker reading passages from 7 non-fiction books, approximately 24 hours in total.
- (will be added more)
Preprocessing
First, run
python3 prepare_align.py config/LJSpeech/preprocess.yaml
for some preparations.
As described in the paper, Montreal Forced Aligner (MFA) is used to obtain the alignments between the utterances and the phoneme sequences.
Alignments for the LJSpeech datasets are provided here from ming024's FastSpeech2.
You have to unzip the files in preprocessed_data/LJSpeech/TextGrid/.
After that, run the preprocessing script by
python3 preprocess.py config/LJSpeech/preprocess.yaml
Alternately, you can align the corpus by yourself.
Download the official MFA package and run
./montreal-forced-aligner/bin/mfa_align raw_data/LJSpeech/ lexicon/librispeech-lexicon.txt english preprocessed_data/LJSpeech
or
./montreal-forced-aligner/bin/mfa_train_and_align raw_data/LJSpeech/ lexicon/librispeech-lexicon.txt preprocessed_data/LJSpeech
to align the corpus and then run the preprocessing script.
python3 preprocess.py config/LJSpeech/preprocess.yaml
Training
Train your model with
python3 train.py -p config/LJSpeech/preprocess.yaml -m config/LJSpeech/model.yaml -t config/LJSpeech/train.yaml
TensorBoard
Use
tensorboard --logdir output/log/LJSpeech
to serve TensorBoard on your localhost.
The loss curves, synthesized mel-spectrograms, and audios are shown.
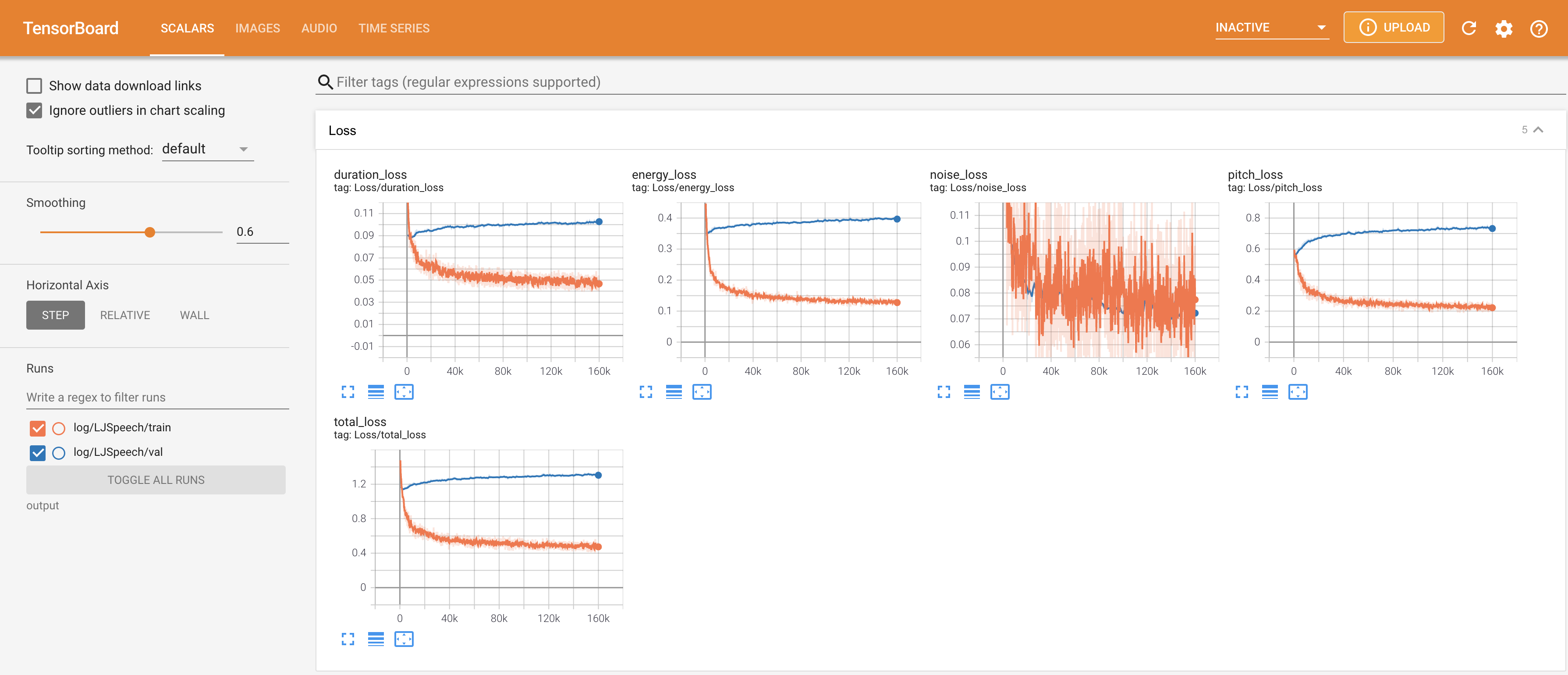
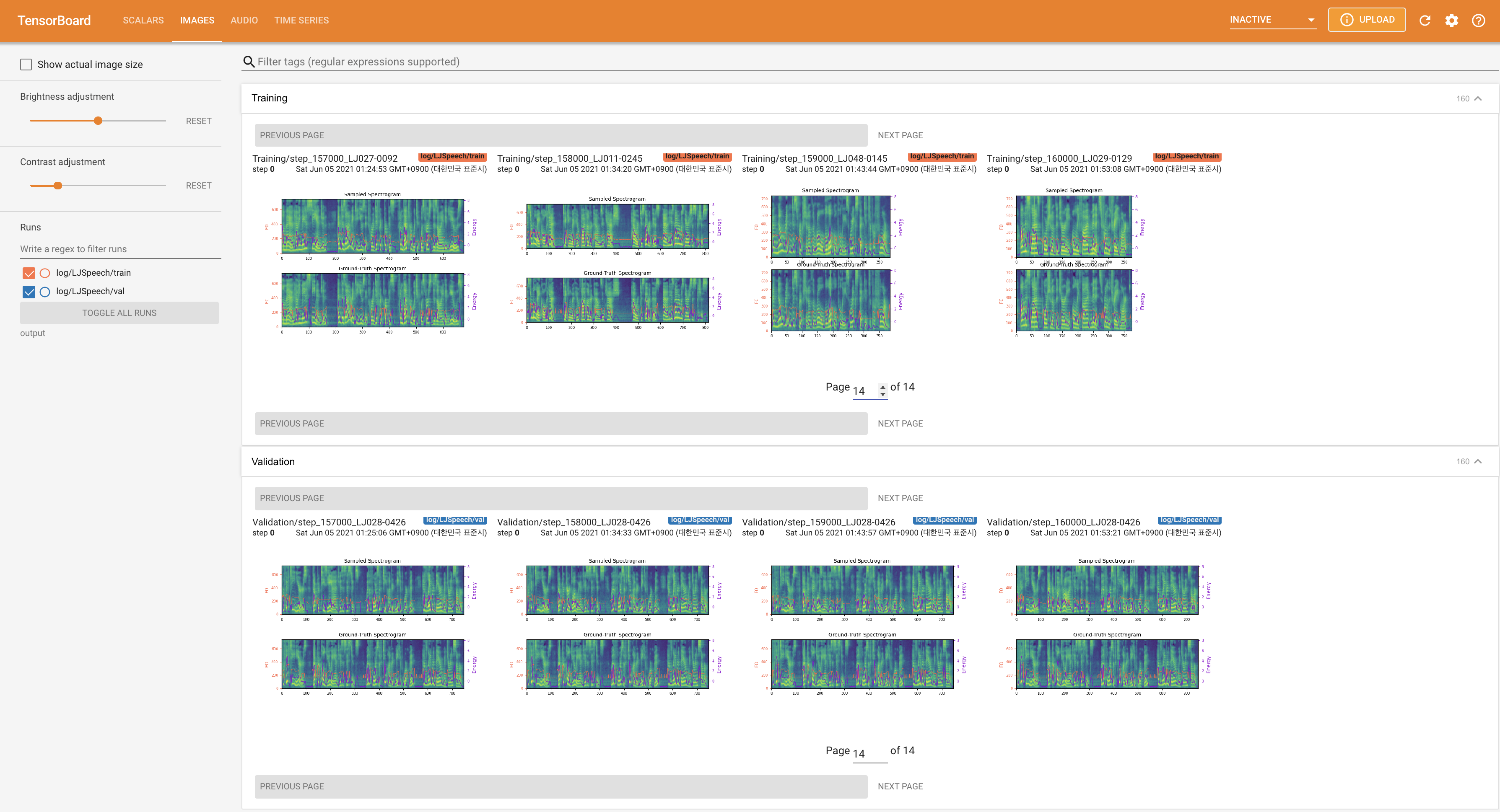
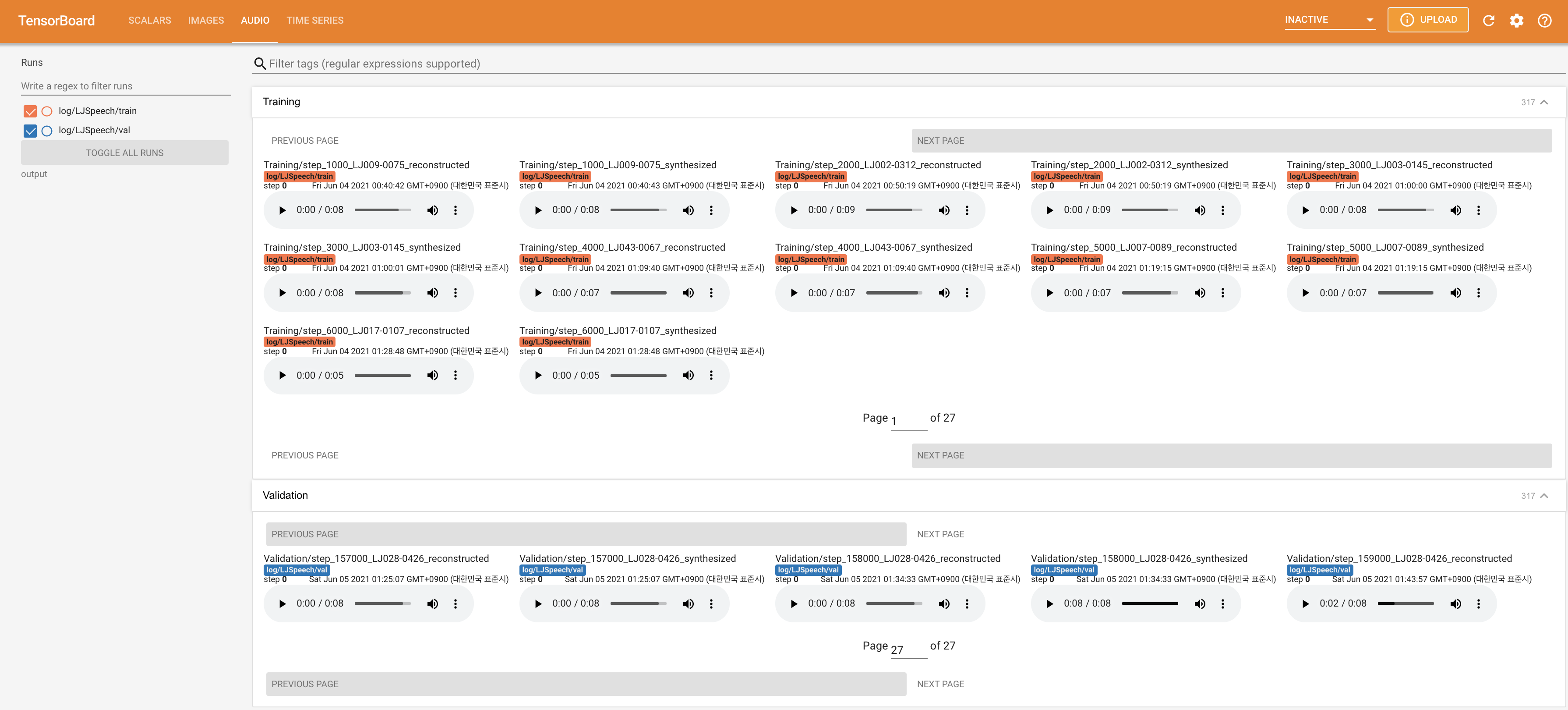
Implementation Issues
- Pitch extractor comparison (on LJ001-0006.wav)
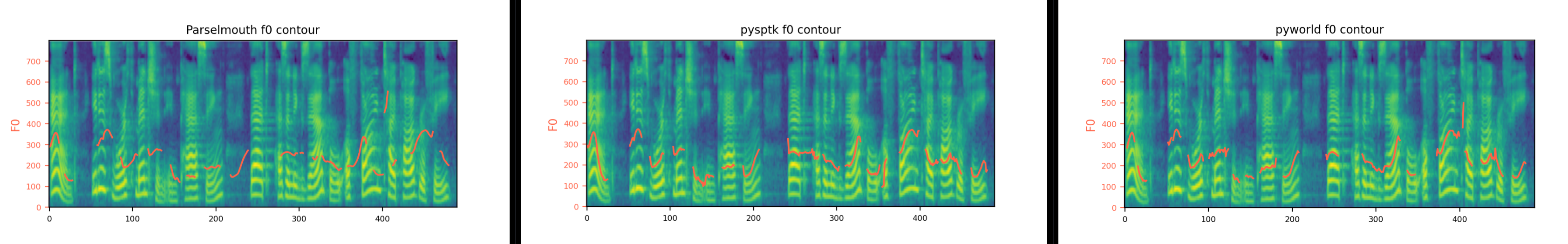
**pyworld** is used to extract f0 (fundamental frequency) as pitch information in this implementation. Empirically, however, I found that all three methods were equally acceptable for clean datasets (e.g., LJSpeech) as above figures. Note that **pysptk** would work better for noisy datasets (as described in [STYLER](https://github.com/keonlee9420/STYLER)).
- Stack two layers of
FFTBlockfor the lyrics encoder (text encoder). - (Naive version) The number of learnable parameters is
34.337M, which is larger than the original paper (26.744M). Thediffusionmodule takes a significant portion of whole parameters. - I did not remove the energy prediction of FastSpeech2 since it is not critical to the model training or performance (as described in LightSpeech). It should be easily removed without any performance degradation.
- Use HiFi-GAN instead of Parallel WaveGAN (PWG) for vocoding.
Citation
@misc{lee2021diffsinger,
author = {Lee, Keon},
title = {DiffSinger},
year = {2021},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/keonlee9420/DiffSinger}}
}



