SeaLion
SeaLion is designed to teach today's aspiring ml-engineers the popular machine learning concepts of today in a way that gives both intuition and ways of application. We do this through concise algorithms that do the job in the least jargon possible and examples to guide you through every step of the way.
Quick Demo
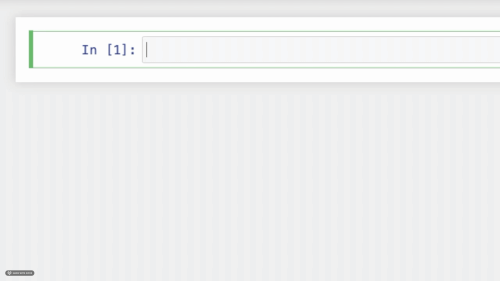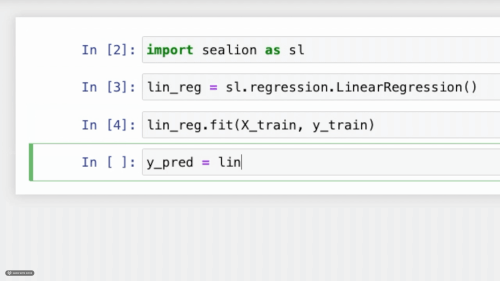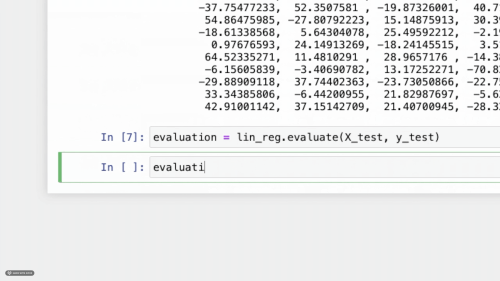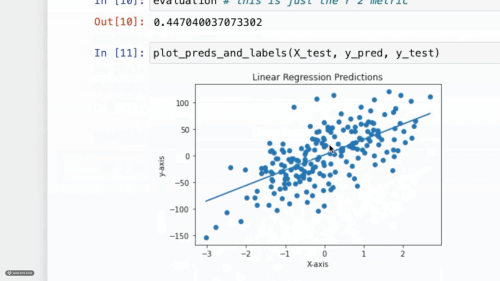
SeaLion in Action
General Usage
For most classifiers you can just do (we'll use Logistic Regression as an
example here) :
from sealion.regression import LogisticRegression
log_reg = LogisticRegression()
to initialize, and then to train :
log_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
and for testing :
y_pred = log_reg.predict(X_test)
evaluation = log_reg.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
For the unsupervised clustering algorithms you may do :
from sealion.unsupervised_clustering import KMeans
kmeans = KMeans(k = 3)
and then to fit and predict :
predictions = kmeans.fit_predict(X)
Neural networks are a bit more complicated, so you may want to check an example
here.
The syntax of the APIs was designed to be easy to use and familiar to most other ML libraries. This is to make sure both beginners and experts in the field
can comfortably use SeaLion. Of course, none of the source code uses other ML frameworks.
Testimonials and Reddit Posts
"Super Expansive Python ML Library"
- @Peter Washington, Stanford PHD candidate in Bio-Engineering
r/Python : r/Python Post
r/learnmachinelearning : r/learningmachinelearning Post
Installation
The package is available on PyPI. Install like such :
pip install sealion
SeaLion can only support Python 3, so please make sure you are on the
newest version.
General Information
SeaLion was built by Anish Lakkapragada, a freshman in high school, starting in Thanksgiving of 2020
and has continued onto early 2021. The library is meant for beginners to
use when solving the standard libraries like iris, breast cancer, swiss
roll, the moons dataset, MNIST, etc. The source code is not as much as
most other ML libraries (only 4000 lines) so it's pretty easy to contribute to. He
hopes to spread machine learning to other high schoolers through this
library.
Documentation
All documentation is currently being put on a website. However useful it
may be, I highly recommend you check the examples posted on GitHub here
to see the usage of the APIs and how it works.
Updates for v4.1 and up!
First things first - thank you for all of the support. The two reddit posts did much better than I expected (1.6k upvotes, about 200 comments) and I got a lot
of feedback and advice. Thank you to anyone who participated in r/Python or r/learnmachinelearning.
SeaLion has also taken off with the posts. We currently have had 3 issues (1 closed) and have reached 195 stars and 20 forks. I wasn't expecting this and I am grateful for everyone who has shown their appreciation for this library.
In versions 4.1+ we are hoping to polish the library more. Currently 4.1 comes with Bernoulli Naive Bayes and we also have added precision, recall, and the f1 metric in the utils module. We are hoping to include Gaussian Mixture Models and Batch Normalization in the future. Code examples for these new algorithms will be created within a day or two after release. Thank you!
Updates for v3.0.0!
SeaLion v3.0 and up has had a lot of major milestones.
The first thing is that all the code examples (in jupyter notebooks) for
basically all of the modules in sealion are put into the examples
directory. Most of them go over using actual datasets like iris, breast
cancer, moons, blobs, MNIST, etc. These were all built using v3.0.8
-hopefully that clears up any confusion. I hope you enjoy them.
Perhaps the biggest change in v3.0 is how we have changed the Cython
compilation. A quick primer on Cython if you are unfamiliar - you take
your python code (in .py files), change it and add some return types and
type declarations, put that in a .pyx file, and compile it to a .so
file. The .so file is then imported in the python module which you use.
The main bug fixed was that the .so file is actually specific to the
architecture of the user. I use macOS and compiled all my files in .so,
so prior v3.0 I would just give those .so files to anybody else. However
other architectures and OSs like Ubuntu would not be able to recognize
those files. Instead what we do know is just store the .pyx files
(universal for all computers) in the source code, and the first time you
import sealion all of those .pyx files will get compiled into .so files
(so they will work for whatever you are using.) This means the first
import will take about 40 seconds, but after that it will be as quick as
any other import.
Machine Learning Algorithms
The machine learning algorithms of SeaLion are listed below. Please note
that the stucture of the listing isn't meant to resemble that of
SeaLion's APIs. Of course, new algorithms are being made right now.
-
Deep Neural Networks
- Optimizers
- Gradient Descent (and mini-batch gradient descent)
- Momentum Optimization w/ Nesterov Accelerated Gradient
- Stochastic gradient descent (w/ momentum + nesterov)
- AdaGrad
- RMSprop
- Adam
- Nadam
- Layers
- Flatten (turn 2D+ data to 2D matrices)
- Dense (fully-connected layers)
- Regularization
- Dropout
- Activations
- ReLU
- Tanh
- Sigmoid
- Softmax
- Leaky ReLU
- ELU
- SELU
- Swish
- Loss Functions
- MSE (for regression)
- CrossEntropy (for classification)
- Transfer Learning
- Save weights (in a pickle file)
- reload them and then enter them into the same neural network
- this is so you don't have to start training from scratch
- Optimizers
-
Regression
- Linear Regression (Normal Equation, closed-form)
- Ridge Regression (L2 regularization, closed-form solution)
- Lasso Regression (L1 regularization)
- Elastic-Net Regression
- Logistic Regression
- Softmax Regression
- Exponential Regression
- Polynomial Regression
-
Dimensionality Reduction
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (tSNE)
-
Unsupervised Clustering
- KMeans (w/ KMeans++)
- DBSCAN
-
Naive Bayes
- Multinomial Naive Bayes
- Gaussian Naive Bayes
- Bernoulli Naive Bayes
-
Trees
- Decision Tree (with max_branches, min_samples regularization +
CART training)
- Decision Tree (with max_branches, min_samples regularization +
-
Ensemble Learning
- Random Forests
- Ensemble/Voting Classifier
-
Nearest Neighbors
- k-nearest neighbors
-
Utils
- one_hot encoder function (one_hot())
- plot confusion matrix function (confusion_matrix())
- revert one hot encoding to 1D Array (revert_one_hot())
- revert softmax predictions to 1D Array (revert_softmax())
Algorithms in progress
Some of the algorithms we are working on right now.
- Batch Normalization
- Gaussian Mixture Models
- Barnes Hut t-SNE (please, please contribute for this one)



