Texar
Texar is an open-source toolkit based on Tensorflow, aiming to support a broad set of machine learning especially text generation tasks, such as machine translation, dialog, summarization, content manipulation, language modeling, and so on. Texar is designed for both researchers and practitioners for fast prototyping and experimentation.
With the design goals of modularity, versatility, and extensibility in mind, Texar extracts the common patterns underlying the diverse tasks and methodologies, creates a library of highly reusable modules and functionalities, and facilitates arbitrary model architectures and algorithmic paradigms, e.g.,
- encoder(s) to decoder(s), sequential- and self-attentions, memory, hierarchical models, classifiers...
- maximum likelihood learning, reinforcement learning, adversarial learning, probabilistic modeling, ...
With Texar, cutting-edge complex models can be easily constructed, freely enriched with best modeling/training practices, readily fitted into standard training/evaluation pipelines, and fastly experimented and evolved by, e.g., plugging-in and swapping-out different modules.
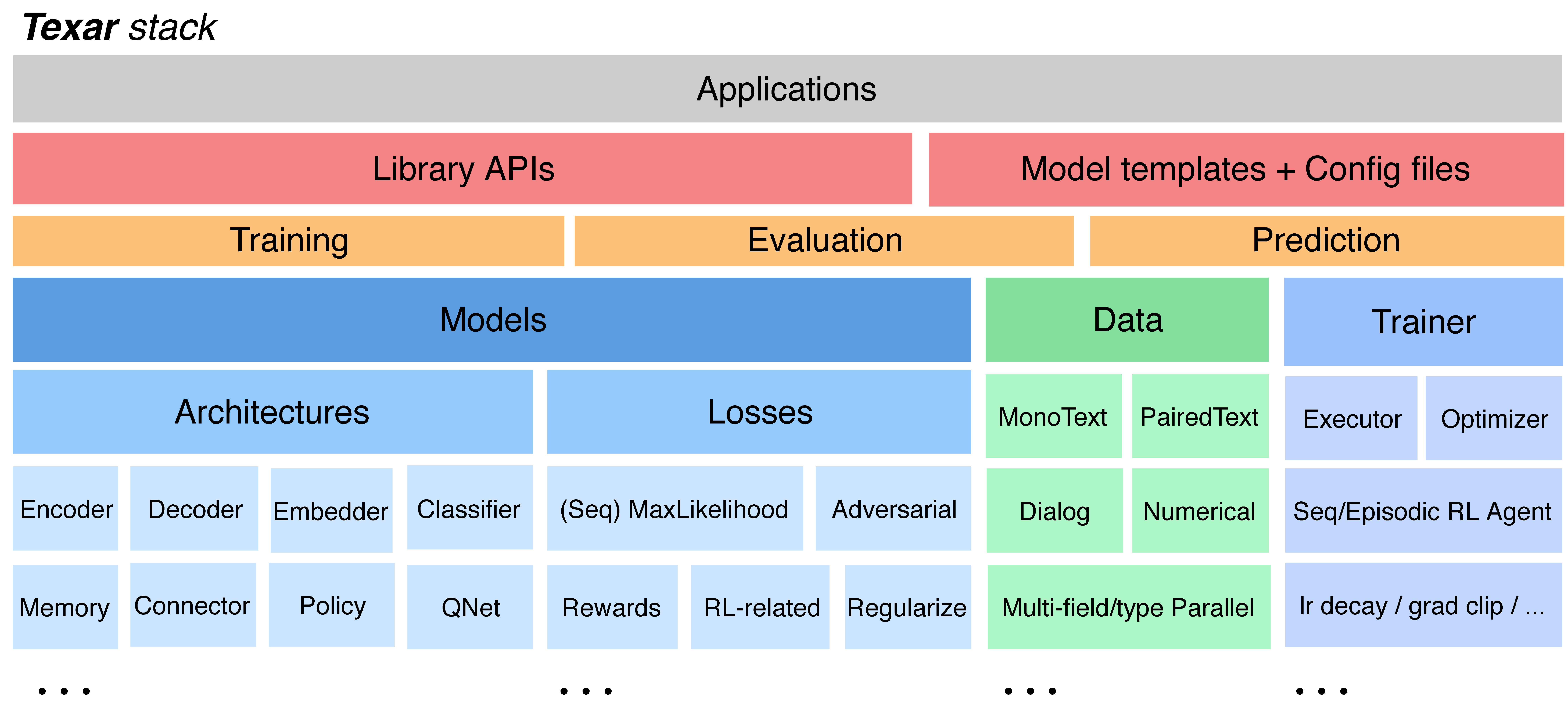
Key Features
- Versatility. Texar contains a wide range of modules and functionalities for composing arbitrary model architectures and implementing various learning algorithms, as well as for data processing, evaluation, prediction, etc.
- Modularity. Texar decomposes diverse complex machine learning models/algorithms into a set of highly-reusable modules. In particular, model architecture, losses, and learning processes are fully decomposed.
Users can construct their own models at a high conceptual level just like assembling building blocks. It is convenient to plug-ins or swap-out modules, and configure rich options of each module. For example, switching between maximum likelihood learning and reinforcement learning involves only changing several lines of code. - Extensibility. It is straightforward to integrate any user-customized, external modules. Also, Texar is fully compatible with the native Tensorflow interfaces and can take advantage of the rich Tensorflow features, and resources from the vibrant open-source community.
- Interfaces with different functionality levels. Users can customize a model through 1) simple Python/YAML configuration files of provided model templates/examples; 2) programming with Python Library APIs for maximal customizability.
- Easy-to-use APIs: 1) Convenient automatic variable re-use---no worry about the complicated TF variable scopes; 2) Pytorch-like callable modules; 3) Rich configuration options for each module, all with default values; ...
- Well-structured high-quality code of uniform design patterns and consistent styles.
Library API Example
Builds a (self-)attentional sequence encoder-decoder model, with different learning algorithms:
import texar as tx
# Data
data = tx.data.PairedTextData(hparams=hparams_data) # Hyperparameter configs in `hparams`
iterator = tx.data.DataIterator(data)
batch = iterator.get_next() # A data mini-batch
# Model architecture
embedder = tx.modules.WordEmbedder(data.target_vocab.size, hparams=hparams_emb)
encoder = tx.modules.TransformerEncoder(hparams=hparams_encoder)
outputs_enc = encoder(inputs=embedder(batch['source_text_ids']),
sequence_length=batch['source_length'])
decoder = tx.modules.AttentionRNNDecoder(memory=output_enc,
memory_sequence_length=batch['source_length'],
hparams=hparams_decoder)
outputs, _, _ = decoder(inputs=embedder(batch['target_text_ids']),
sequence_length=batch['target_length']-1)
# Loss for maximum likelihood learning
loss = tx.losses.sequence_sparse_softmax_cross_entropy(
labels=batch['target_text_ids'][:, 1:],
logits=outputs.logits,
sequence_length=batch['target_length']-1) # Automatic masks
# Beam search decoding
outputs_bs, _, _ = tx.modules.beam_search_decode(
decoder,
embedding=embedder,
start_tokens=[data.target_vocab.bos_token_id]*num_samples,
end_token=data.target_vocab.eos_token_id)
# Policy gradient agent for RL learning
agent = tx.agents.SeqPGAgent(samples=outputs.sample_id,
logits=outputs.logits,
sequence_length=batch['target_length']-1,
hparams=config_model.agent)
Installtion
git clone https://github.com/asyml/texar.git
cd texar
pip install -e .
Getting Started
Reference
If you use Texar, please cite the report with the following BibTex entry:
Texar: A Modularized, Versatile, and Extensible Toolkit for Text Generation
Zhiting Hu, Haoran Shi, Zichao Yang, Bowen Tan, Tiancheng Zhao, Junxian He, Wentao Wang, Xingjiang Yu, Lianhui Qin, Di Wang, Xuezhe Ma, Hector Liu, Xiaodan Liang, Wanrong Zhu, Devendra Singh Sachan, Eric P. Xing
2018
@article{hu2018texar,
title={Texar: A Modularized, Versatile, and Extensible Toolkit for Text Generation},
author={Hu, Zhiting and Shi, Haoran and Yang, Zichao and Tan, Bowen and Zhao, Tiancheng and He, Junxian and Wang, Wentao and Yu, Xingjiang and Qin, Lianhui and Wang, Di and Ma, Xuezhe and Liu, Hector and Liang, Xiaodan and Zhu, Wanrong and Sachan, Devendra Singh and Xing, Eric},
year={2018}
}



