Forte
Forte is a toolkit for building Natural Language Processing pipelines, featuring cross-task interaction, adaptable data-model interfaces and many more. It provides a platform to assemble state-of-the-art NLP and ML technologies in a highly-composable fashion, including a wide spectrum of tasks ranging from Information Retrieval, Natural Language Understanding to Natural Language Generation.
With Forte, it is extremely simple to build an integrated system that can search documents, analyze and extract information and generate language all in one place. This allows the developer to fully utilize and combine the strength and results from each step, and allow the system to make fully informed decision at the end of the pipeline.
While it is quite easy to combine arbitrary 3rd party tools (Check out these examples!), Forte also brings technology to you by supporting deep learning via Texar, and by providing a convenient model data interface that allows user to cast tasks to models.
Core Design Principles
The core design principle of Forte is the abstraction of NLP concepts and machine learning models,
which provides better separation between data, model and tasks, but enables interactions
between different components of the pipeline. Based on this, we make Forte:
-
Composable: Forte helps users to decompose a problem into data, models and tasks.
The tasks can further be divided into sub-tasks. A complex use case
can be solved by composing heterogeneous modules via straightforward python APIs or declarative
configuration files. The components (e.g. models or tasks) in the pipeline can be flexibly
swapped in and out, as long as the API contracts are matched. The approach greatly improves module
reusability, enables fast development and makes the library flexible for user needs. -
Generalizable and Extensible: Forte promotes generalization to support not only a wide
range of NLP tasks, but also extensible for new tasks or new domains. In particular, Forte
provides the Ontology system that helps users define types according to their tasks.
Users can simply specify the type declaratively through JSON files. Our Code Generation tool
will automatically generate python files ready to be used into your project. Check out our
Ontology Generation documentation for more details. -
Transparent Data Flow: Central to Forte's composable architecture is a universal data
format that supports seamless data flow between different steps. Forte advocates a transparent
data flow to facilitate flexible process intervention and simple pipeline control. Combined with
the general data format, Forte makes a perfect tool for data inspection, component swapping and
result sharing. This is particularly helpful during team collaborations!
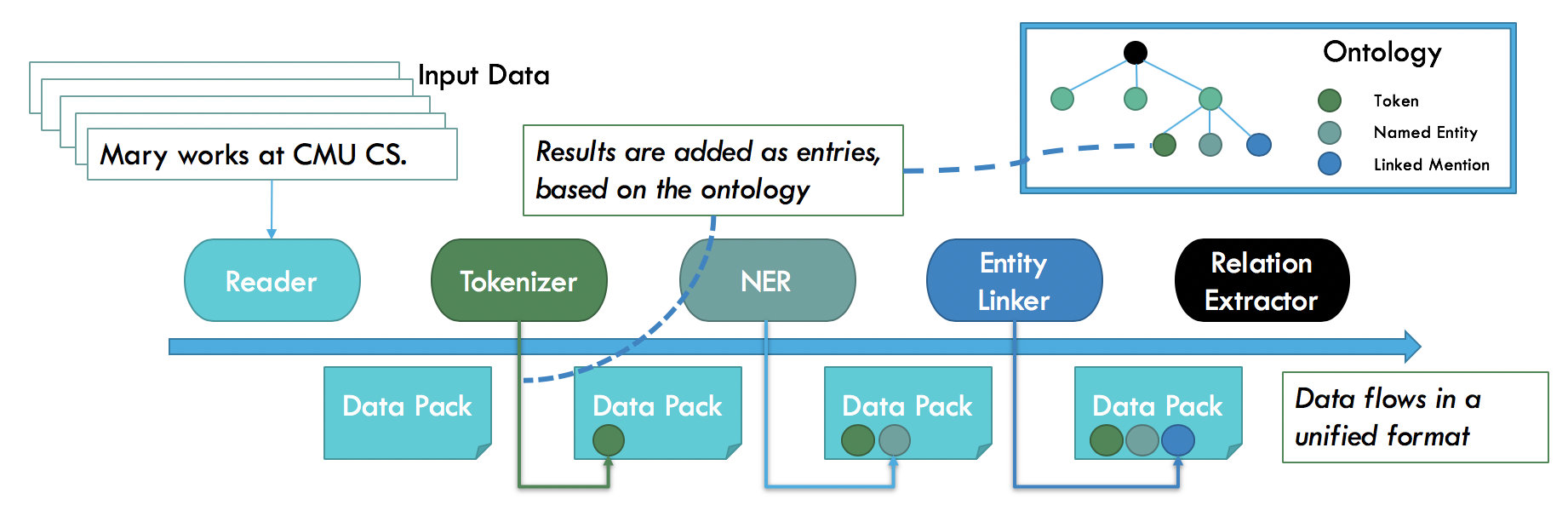
A high level Architecture of Forte showing how ontology and entries work with the pipeline.
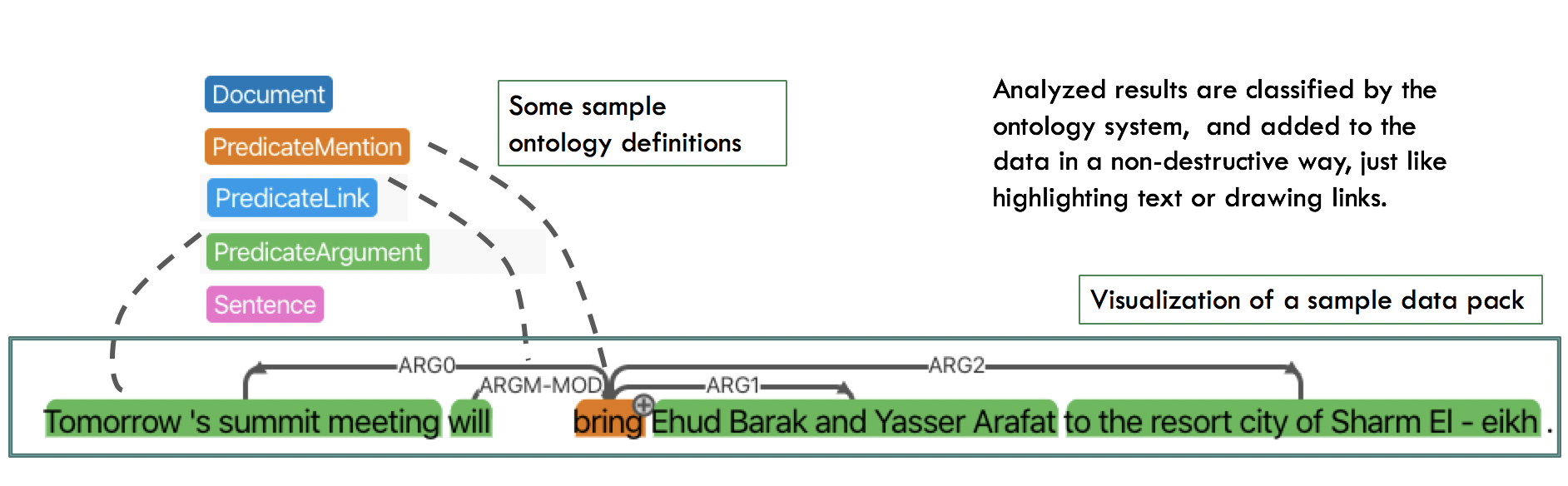
Forte stores results in data packs and use the ontology to represent task logic
Package Overview
| forte | an open-source toolkit for NLP |
| forte.data.readers | a data module for reading different formats of text data like CoNLL, Ontonotes etc |
| forte.processors | a collection of processors for building NLP pipelines |
| forte.trainer | a collection of modules for training different NLP tasks |
| ft.onto.base_ontology | a module containing basic ontologies like Token, Sentence, Document etc |
Library API example
A simple code example that runs Named Entity Recognizer
import yaml
from texar.torch import HParams
from forte.pipeline import Pipeline
from forte.data.readers import CoNLL03Reader
from forte.processors import CoNLLNERPredictor
from ft.onto.base_ontology import Token, Sentence, EntityMention
config_data = yaml.safe_load(open("config_data.yml", "r"))
config_model = yaml.safe_load(open("config_model.yml", "r"))
config = HParams({}, default_hparams=None)
config.add_hparam('config_data', config_data)
config.add_hparam('config_model', config_model)
pl = Pipeline()
pl.set_reader(CoNLL03Reader())
pl.add_processor(CoNLLNERPredictor(), config=config)
pl.initialize()
for pack in pl.process_dataset(config.config_data.test_path):
for pred_sentence in pack.get_data(context_type=Sentence, request={Token: {"fields": ["ner"]}}):
print("============================")
print(pred_sentence["context"])
print("The entities are...")
print(pred_sentence["Token"]["ner"])
print("============================")
Many more examples are available here.
Download and Installation
Download the repository through
git clone https://github.com/asyml/forte.git
After cd into forte, you can install it through
pip install .




