International Space Station data with Python research?
Plotting ISS trajectory, calculating the velocity over the earth and more.
Plotting trajectory:
We are going to make a graph of the trajectory of the ISS that is N minutes long. The N will be chosen by the user according to their preferences. This means that the program will run and keep points in a list for N minutes.
We will use an API to retrieve ISS current position in latitude and longitude:
http://open-notify.org/Open-Notify-API/ISS-Location-Now/
First we need to import the following python modules:
Pandas to read json data from ISS API, plotly to make the plot of the trajectory and time to time.sleep function
import pandas as pd
import plotly.express as px
import time
Second we must initialize the list that will preserve the latitude and longitude points (every sixty seconds). You also have to initialize the N variable with time in minutes
latitudes = []
longitudes = []
N = 60 # Sixty for one hour trajectory
Then we will create the following for loop to keep recording latitude-longitude points separated by one minute
We use for i in range(N), which is the time that the script will keep running (in hours) because we have a time.sleep(60) at the end
for i in range(N):
url = "http://api.open-notify.org/iss-now.json" # API URL
df = pd.read_json(url) # Pandas read JSON data from API
latitudes.append(df["iss_position"]["latitude"]) # We append latitude ISS position to latitudes list
longitudes.append(df["iss_position"]["longitude"]) # We append longitude ISS position to longitudes list
time.sleep(60) # This is used to separate de point records with one minute
When the for loop finish the iterating we will have a record of N minutes ISS trajectory. Now we can plot this with Plotly (px.line_geo):
px.line_geo will create a plot with earth map
fig = px.line_geo(lat=latitudes, lon=longitudes) # Passing our latitudes and longitudes list as parameter
fig.show()
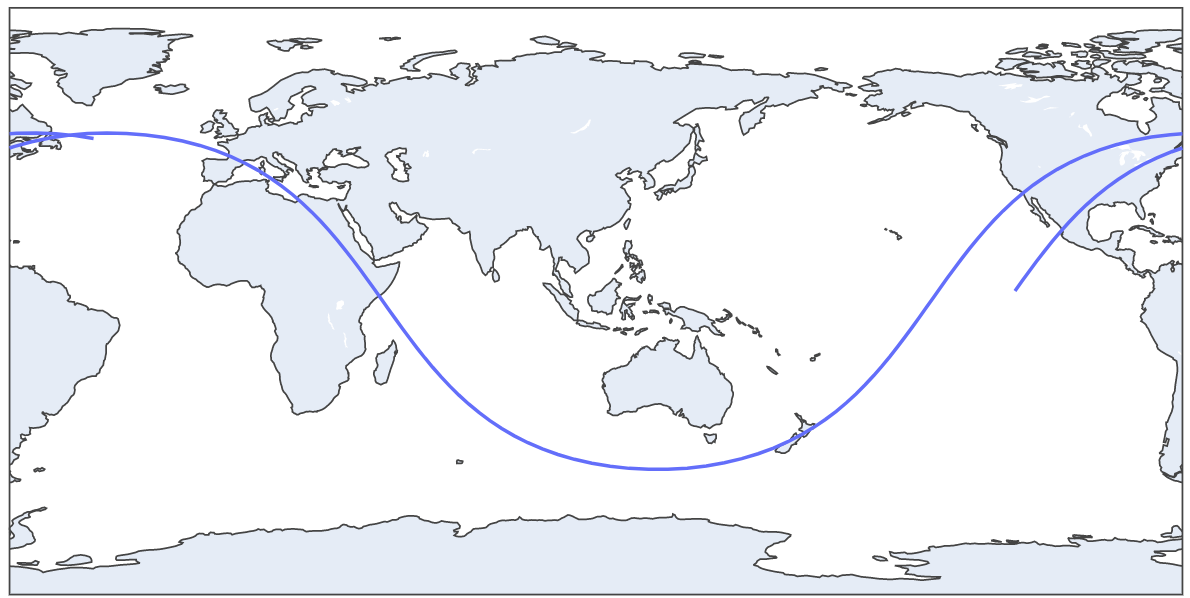
This is a two hours trajectory plot
We can update our plot to orthographic projection with this code:
fig.update_geos(projection_type="orthographic")
fig.update_layout(height=300, margin={"r":0,"t":0,"l":0,"b":0})
fig.show()
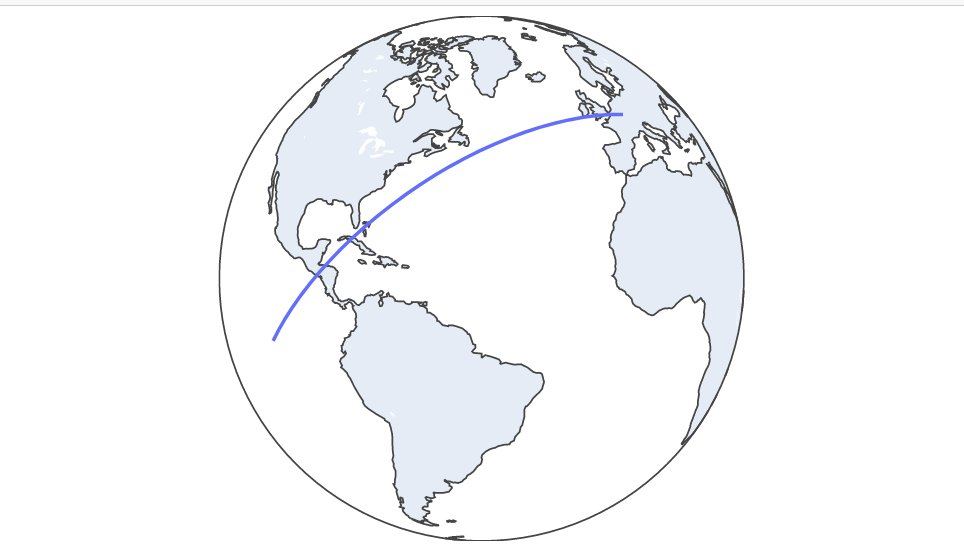
30 minutes trajectory plot
2 Hours trajectory plot GIF
Estimating ISS velocity:
We will estimate the ISS velocity using two diferent latitude-longitude points separated by one minute (sixty seconds). We can get the distance between that two points and then use phisics formula velocity(m/s) = distance(in meters)/time(in seconds)
First import the following python modules
import pandas as pd # Pandas to read API data
import time # Time for time.sleep
import geopy.distance # Geopy to get distance between two lat-lon points
import requests # Get another API data
import json # Read that data
We need to initialize two empty list to save latitudes and longitudes
lat = []
long = []
Next we will use a for loop to get the two latitude-longitude points separated by 60 seconds (time.sleep(60))
for i in range(2): # for in range(2) because we want two lat-lon points
url = "http://api.open-notify.org/iss-now.json" # API url
df = pd.read_json(url) # Read API Json data with Pandas
lat.append(df["iss_position"]["latitude"]) # Append latitude to lat list
long.append(df["iss_position"]["longitude"]) # Append longitude to long list
time.sleep(60) # Wait 60 seconds to record the second lat-lon point
When this for loop finish we will have a lat list with two latitude positions and one long list with two longitude positions. In conjuntion of this 4 numbers we have two lat-lon points in different time moments (separated by one minute)
Then we must get the distance between this points:
We create the two different points. The first one with lat[0] index and long[0]. The second one with lat[1] and long[0]
coords_1 = (lat[0], long[0])
coords_2 = (lat[1], long[1])
Then calculate distance with geopy library:
distance = (
geopy.distance.distance(coords_1, coords_2).m
) # Distance between the points in meters
But we must make a litle correction. Because ISS isn’t moving in earth surface. It’s orbiting aproximately 400Km above earth surface. So the radius is greater. The distance traveled is a litle bit more. To do this, we need to get ISS current altitud. Use the following code:
iss_alt_url = "https://api.wheretheiss.at/v1/satellites/25544"
r = requests.get(iss_alt_url)
r = r.text
r = json.loads(r)
iss_alt = int(r["altitude"]) # IN KM
Now apply phisics formula to make the correction
earth_radius = 6371 # in KM
distance_corrected = (distance * (earth_radius+iss_alt)/earth_radius)
Now finish the calculation with speed formula already explained:
speed = distancia_corrected/60
print(round(speed*3.6, 3), "KM/H") # Multiplied by 3.6 to convert from m/s to km/h. Rounded by 3.
Output:
26367.118 KM/h